리눅스 / RAID / Linear RAID, RAID0, RAID1, RAID5, RAID6
Created 2021-10-14
Last Modified 2021-10-14
RAID 뜻과 종류
RAID
- Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disk or Redundant Array of Independent Disk
- 여러 개의 하드디스크를 하나처럼 사용하게 하는 기술. 예를 들어 1TB 하드디스크 두 개를 묶어서 2TB 하드디스크처럼 사용할 수 있다.
- 크게 하드웨어 RAID와 소프트웨어 RAID로 구분할 수 있다.
- 하드웨어 RAID는 성능이 좋으나 비싸다.
- 소프트웨어 RAID는 운영체제에서 지원하는 것으로 OS RAID라고도 한다.
Linear RAID
- 두 개 이상의 하드디스크를 하나처럼 사용하는 가장 단순한 RAID.
- 1TB + 2TB + 3TB = 6TB
- 순차적으로 하드디스크 사용. 예를 들어 A, B, C 하드디스크로 Linear RAID를 구성했다면 A에 먼저 데이터를 저장하고 A가 꽉 차면 B에 저장.
- RAID에 속한 디스크가 손상되어도, 손상되지 않은 디스크에 있는 데이터는 살아 있음.
RAID0
- 두 개 이상의 하드디스크를 하나처럼 사용하는데, 저장은 디스크에 분배하여 저장한다. 예를 들어 A, B, C 디스크에 파일을 저장하면 1/3씩 나누어 각각의 디스크에 저장.
- 하나의 디스크가 꽉 차면 분배가 불가능하므로 작은 크기의 하드디스크 용량에 맞춰진다.
- 1TB + 2TB + 3TB = 3TB (각 디스크마다 1TB 만큼만 사용 가능)
- Linear RAID에 비하여 속도가 빠르지만, 하나의 디스크만 고장 나도 모든 데이터가 손실된다.
RAID1
- 데이터를 하드디스크 여러 디스크에 중복하여 저장하는 것으로 데이터 보존에 중점을 둔 방식.
- 하나의 디스크가 꽉 차면 동시 저장이 불가능하므로 작은 크기의 하드디스크 용량에 맞춰진다.
- 1TB + 2TB = 1TB
- 하나의 하드디스크만 정상이어도 데이터 손실이 없음.
RAID5
- 세 개 이상의 하드디스크를 묶는 RAID.
- 모든 하드디스크에 분배하여 저장하고, Parity 한 개 사용.
- 한 개의 하드디스크가 고장 나도 데이터 손실이 없음.
- 1TB + 1TB + 1TB + 1TB = 3TB
RAID6
- 네 개 이상의 하드디스크 필요.
- 모든 하드디스크에 분배하여 저장하고, Parity 두 개 사용.
- 두 개의 하드디스크가 고장 나도 데이터 손실이 없음.
- 1TB + 1TB + 1TB + 1TB + 1TB = 3TB
- RAID5에 비하여 성능이 떨어짐.
RAID용 파티션 만들기
- fdisk 명령어로 디스크에 파티션을 만든다. 파티션의 Hex code는 fd로 한다.
- 예를 들어 /dev/sdb에 파티션을 만든다면 다음과 같이 한다.
- n → 엔터 4번 → t → fd → w
# fdisk /dev/sdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
First sector (2048-209715199, default 2048):
Using default value 2048
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-209715199, default 209715199):
Using default value 209715199
Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 100 GiB is set
Command (m for help): t
Selected partition 1
Hex code (type L to list all codes): fd
Changed type of partition 'Linux' to 'Linux raid autodetect'
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
- RAID에 사용할 디스크는 모두 위와 같이 작업한다.
- 아래는 RAID 구성에 사용할 디스크 9개를 장착하고 파티션을 만든 결과이다.
# ls -l /dev/sd* brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 0 Oct 12 19:13 /dev/sda brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 1 Oct 12 19:13 /dev/sda1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 2 Oct 12 19:13 /dev/sda2 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 16 Oct 12 19:33 /dev/sdb brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 17 Oct 12 19:33 /dev/sdb1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 32 Oct 12 19:34 /dev/sdc brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 33 Oct 12 19:34 /dev/sdc1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 48 Oct 12 19:34 /dev/sdd brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 49 Oct 12 19:34 /dev/sdd1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 64 Oct 12 19:36 /dev/sde brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 65 Oct 12 19:36 /dev/sde1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 80 Oct 12 19:34 /dev/sdf brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 81 Oct 12 19:34 /dev/sdf1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 96 Oct 12 19:34 /dev/sdg brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 97 Oct 12 19:34 /dev/sdg1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 112 Oct 12 19:35 /dev/sdh brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 113 Oct 12 19:35 /dev/sdh1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 128 Oct 12 19:35 /dev/sdi brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 129 Oct 12 19:35 /dev/sdi1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 144 Oct 12 19:35 /dev/sdj brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 145 Oct 12 19:35 /dev/sdj1
RAID 만들기
목표는 아래와 같이 RAID를 구성하는 것.
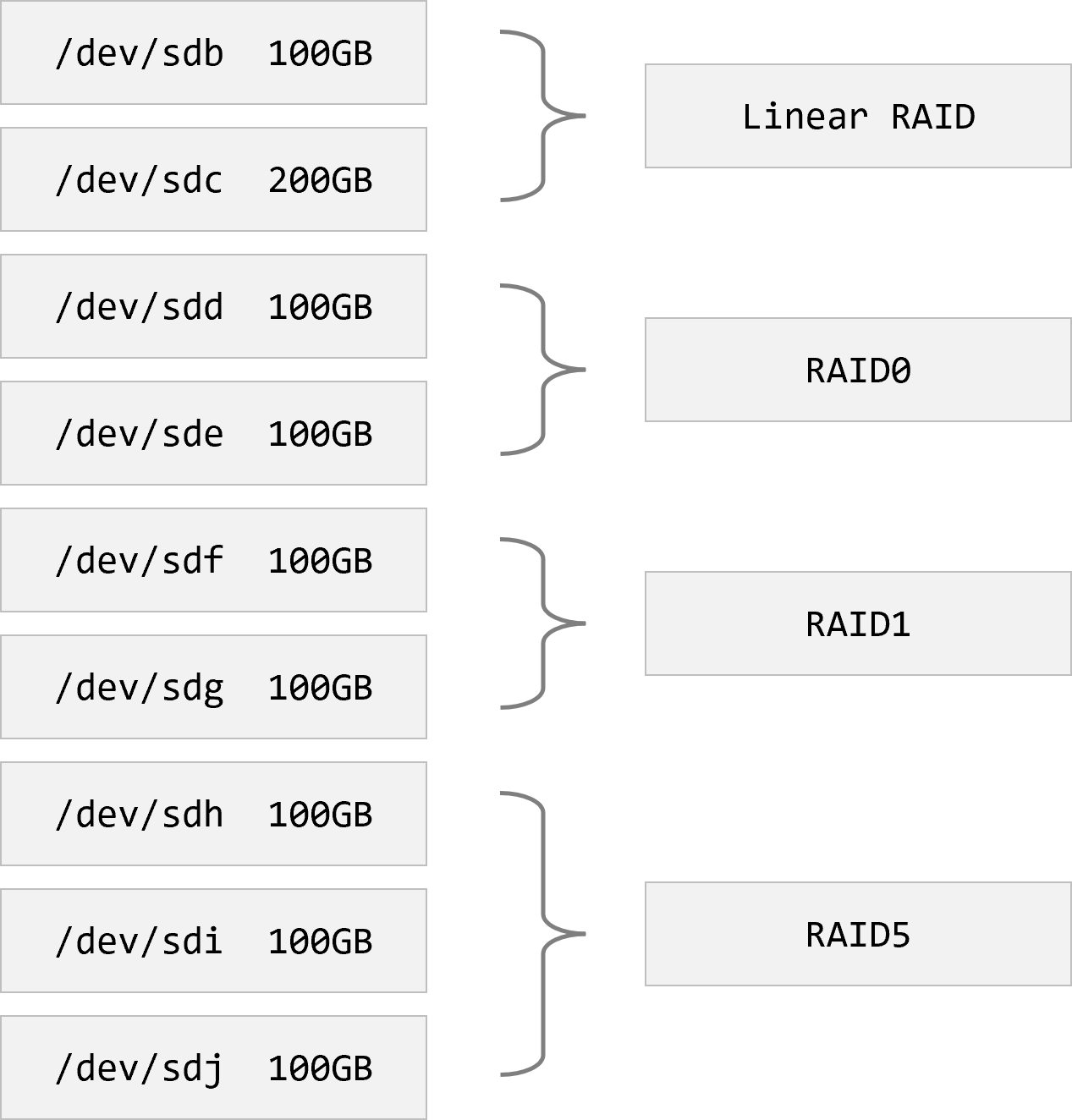
- 다음과 같이 명령하여 Linear RAID를 만든다.
- /dev/md1 : 접근할 수 있는 이름. 이름은 /dev/md9처럼 md 뒤에 숫자를 붙여서 만든다.
- --level=linear : Linear RAID를 만들겠다는 뜻. linear 대신 0, 1, 5, 6을 쓰면 RAID0, RAID1, RAID5, RAID6을 만든다.
- --raid-devices=2 : 두 개의 디스크를 사용하겠다는 뜻.
# mdadm --create /dev/md1 --level=linear --raid-devices=2 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1 mdadm: Defaulting to version 1.2 metadata mdadm: array /dev/md1 started.
- 레이드 정보는 mdadm 명령어의 --detail 옵션으로 볼 수 있다.
# mdadm --detail /dev/md1
/dev/md1:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Wed Oct 13 19:00:59 2021
Raid Level : linear
Array Size : 314437632 (299.87 GiB 321.98 GB)
Raid Devices : 2
Total Devices : 2
Persistence : Superblock is persistent
Update Time : Wed Oct 13 19:00:59 2021
State : clean
Active Devices : 2
Working Devices : 2
Failed Devices : 0
Spare Devices : 0
Rounding : 0K
Consistency Policy : none
Name : centos-7-01:1 (local to host centos-7-01)
UUID : 2fbd4f18:2ba78530:0688808c:ce3614dd
Events : 0
Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
0 8 17 0 active sync /dev/sdb1
1 8 33 1 active sync /dev/sdc1
- 다음과 같이 명령하여 RAID0를 만든다.
# mdadm --create /dev/md2 --level=0 --raid-devices=2 /dev/sdd1 /dev/sde1 mdadm: Defaulting to version 1.2 metadata mdadm: array /dev/md2 started.
# mdadm --detail /dev/md2
/dev/md2:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Wed Oct 13 19:01:48 2021
Raid Level : raid0
Array Size : 209580032 (199.87 GiB 214.61 GB)
Raid Devices : 2
Total Devices : 2
Persistence : Superblock is persistent
Update Time : Wed Oct 13 19:01:48 2021
State : clean
Active Devices : 2
Working Devices : 2
Failed Devices : 0
Spare Devices : 0
Chunk Size : 512K
Consistency Policy : none
Name : centos-7-01:2 (local to host centos-7-01)
UUID : 042ff5cb:d504b4ea:d5bfdceb:8f639b76
Events : 0
Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
0 8 49 0 active sync /dev/sdd1
1 8 65 1 active sync /dev/sde1
- 다음과 같이 명령하여 RAID1을 만든다.
# mdadm --create /dev/md3 --level=1 --raid-devices=2 /dev/sdf1 /dev/sdg1
mdadm: Note: this array has metadata at the start and
may not be suitable as a boot device. If you plan to
store '/boot' on this device please ensure that
your boot-loader understands md/v1.x metadata, or use
--metadata=0.90
Continue creating array? y
mdadm: Defaulting to version 1.2 metadata
mdadm: array /dev/md3 started.
# mdadm --detail /dev/md3
/dev/md3:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Wed Oct 13 19:02:53 2021
Raid Level : raid1
Array Size : 104790016 (99.94 GiB 107.30 GB)
Used Dev Size : 104790016 (99.94 GiB 107.30 GB)
Raid Devices : 2
Total Devices : 2
Persistence : Superblock is persistent
Update Time : Wed Oct 13 19:13:32 2021
State : clean, resyncing
Active Devices : 2
Working Devices : 2
Failed Devices : 0
Spare Devices : 0
Consistency Policy : resync
Resync Status : 55% complete
Name : centos-7-01:3 (local to host centos-7-01)
UUID : e562257d:8aea50ad:d1c94c37:4bd39d94
Events : 10
Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
0 8 81 0 active sync /dev/sdf1
1 8 97 1 active sync /dev/sdg1
- 다음과 같이 명령하여 RAID5를 만든다.
# mdadm --create /dev/md4 --level=5 --raid-devices=3 /dev/sdh1 /dev/sdi1 /dev/sdj1 mdadm: Defaulting to version 1.2 metadata mdadm: array /dev/md4 started.
# mdadm --detail /dev/md4
/dev/md4:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Wed Oct 13 19:03:29 2021
Raid Level : raid5
Array Size : 209580032 (199.87 GiB 214.61 GB)
Used Dev Size : 104790016 (99.94 GiB 107.30 GB)
Raid Devices : 3
Total Devices : 3
Persistence : Superblock is persistent
Update Time : Wed Oct 13 19:34:40 2021
State : clean
Active Devices : 3
Working Devices : 3
Failed Devices : 0
Spare Devices : 0
Layout : left-symmetric
Chunk Size : 512K
Consistency Policy : resync
Name : centos-7-01:4 (local to host centos-7-01)
UUID : 7136aaa7:624fb41e:07dc4a32:b24b605b
Events : 1156
Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
0 8 113 0 active sync /dev/sdh1
1 8 129 1 active sync /dev/sdi1
3 8 145 2 active sync /dev/sdj1
- RAID 목록은 다음과 같이 명령하여 볼 수 있다.
# ls -l /dev/md* brw-rw----. 1 root disk 9, 1 Oct 13 19:00 /dev/md1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 9, 2 Oct 13 19:01 /dev/md2 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 9, 3 Oct 13 19:02 /dev/md3 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 9, 4 Oct 13 19:03 /dev/md4
포맷하고 마운트 하기
- 일반 파티션과 마찬가지 방식으로 포맷한다.
- 아래는 /dev/md1을 ext4 형식으로 포맷하는 것. 마찬가지 방식으로 /dev/md2, /dev/md3, /dev/md4를 포맷한다.
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/md1
mke2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
19652608 inodes, 78609408 blocks
3930470 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=2227175424
2399 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000, 7962624, 11239424, 20480000, 23887872, 71663616
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
- 마운트할 폴더를 만든다.
mkdir /RAIDL /RAID0 /RAID1 /RAID5
- 마운트 한다.
# mount /dev/md1 /RAIDL # mount /dev/md2 /RAID0 # mount /dev/md3 /RAID1 # mount /dev/md4 /RAID5
- 아래는 마운트 한 결과. 사이즈를 주의 깊게 보자.
# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on devtmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev tmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 1.9G 9.4M 1.9G 1% /run tmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/mapper/centos-root 50G 4.3G 46G 9% / /dev/mapper/centos-home 969G 37M 969G 1% /home /dev/sda1 1014M 239M 776M 24% /boot tmpfs 379M 12K 379M 1% /run/user/42 tmpfs 379M 0 379M 0% /run/user/0 /dev/md1 296G 65M 280G 1% /RAIDL /dev/md2 197G 61M 187G 1% /RAID0 /dev/md3 99G 61M 94G 1% /RAID1 /dev/md4 197G 61M 187G 1% /RAID5
장애 발생 시 복구하는 방법
- 예를 들어 /dev/md3에 속한 /dev/sdg가 망가져서 제거했다고 하자. 그래도 여전히 데이터는 사용할 수 있다.
- RAID 정보에는 파티션이 제거되었다고 나온다.
# mdadm --detail /dev/md3
/dev/md3:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Wed Oct 13 19:02:53 2021
Raid Level : raid1
Array Size : 104790016 (99.94 GiB 107.30 GB)
Used Dev Size : 104790016 (99.94 GiB 107.30 GB)
Raid Devices : 2
Total Devices : 1
Persistence : Superblock is persistent
Update Time : Wed Oct 13 19:43:12 2021
State : clean, degraded
Active Devices : 1
Working Devices : 1
Failed Devices : 0
Spare Devices : 0
Consistency Policy : resync
Name : centos-7-01:3 (local to host centos-7-01)
UUID : e562257d:8aea50ad:d1c94c37:4bd39d94
Events : 850
Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
- 0 0 0 removed
1 8 81 1 active sync /dev/sdf1
- 새 디스크를 장착하고, 레이드용 파티션을 만든다.
- 파티션이 /dev/sdj1이라면, 아래와 같이 명령하여 /dev/md3에 추가한다.
# mdadm /dev/md3 --add /dev/sdj1 mdadm: added /dev/sdj1
- RAID 정보를 보면 리빌딩 한다고 나오고, 충분한 시간이 지나면 RAID 복구가 완료된다.
# mdadm --detail /dev/md3
/dev/md3:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Wed Oct 13 19:02:53 2021
Raid Level : raid1
Array Size : 104790016 (99.94 GiB 107.30 GB)
Used Dev Size : 104790016 (99.94 GiB 107.30 GB)
Raid Devices : 2
Total Devices : 2
Persistence : Superblock is persistent
Update Time : Wed Oct 13 23:08:02 2021
State : clean, degraded, recovering
Active Devices : 1
Working Devices : 2
Failed Devices : 0
Spare Devices : 1
Consistency Policy : resync
Rebuild Status : 5% complete
Name : centos-7-01:3 (local to host centos-7-01)
UUID : e562257d:8aea50ad:d1c94c37:4bd39d94
Events : 875
Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
2 8 145 0 spare rebuilding /dev/sdj1
1 8 81 1 active sync /dev/sdf1
RAID 제거하기
예를 들어 /dev/md1로 레이드를 만들었다면, 다음과 같이 제거한다.
- 마운트가 되어 있다면 해제한다.
# umount /dev/md1
- 레이드를 정지한다.
# mdadm --stop /dev/md1
- 레이드에 속해있던 파티션에 있는 레이드 정보를 제거한다. 예를 들어 /dev/sdb1에 있는 레이드 정보를 제거하려면 다음과 같이 명령한다.
# mdadm --zero-superblock /dev/sdb1


