리눅스 / 명령어 / ls / 디렉토리와 파일 목록 출력하는 명령어
Created 2018-10-12
Last Modified 2024-01-05
ls는 list의 약어로, 디렉토리와 파일 목록을 출력하는 명령어이다.
ls 디렉토리명
- 디렉토리에 속한 디렉토리와 파일 목록을 출력한다.
- 숨김 파일은 나오지 않는다.
- 디렉토리명을 생략하면 현재 디렉토리에 속한 디렉토리와 파일 목록을 출력한다.
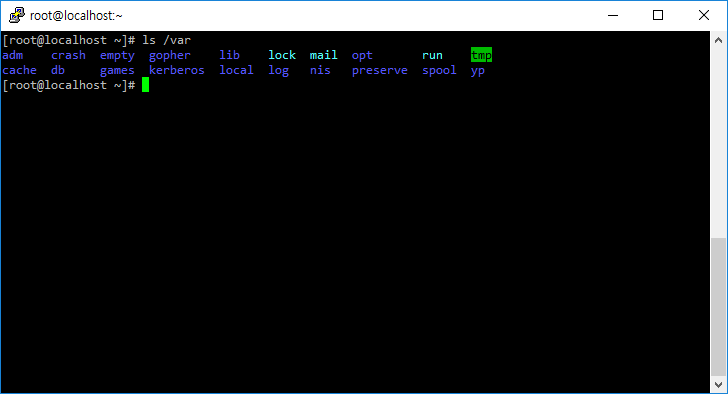
- 예를 들어 다음과 같이 명령하면 /var 디렉토리에 속한 디렉토리와 파일 목록을 출력한다.
# ls /var
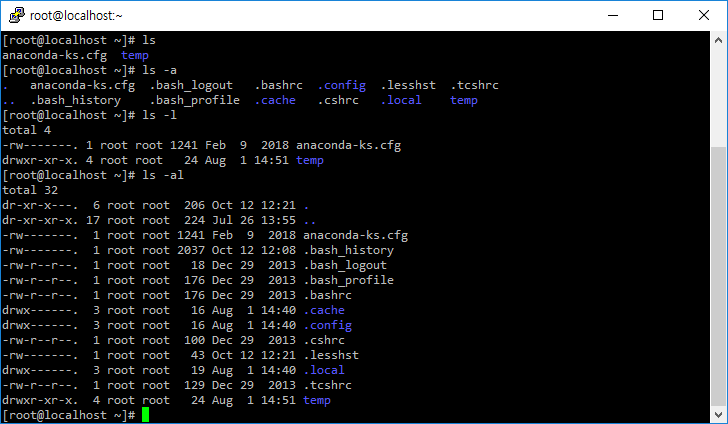
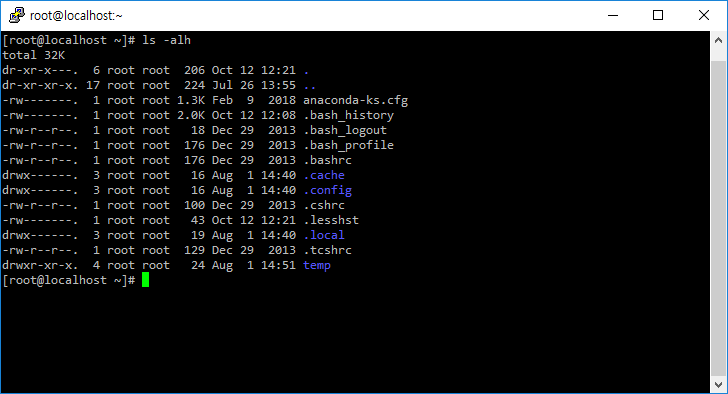
ls -a, ls -l
- -a 옵션을 붙이면 숨김 파일도 출력한다.
- -l 옵션을 붙이면 소유자, 파일 크기 등 자세한 정보도 같이 출력한다.
- -al 옵션을 붙이면 숨김 파일을 포함하여 자세한 정보를 출력한다.
제일 앞에 d가 있는 것은 디렉토리(폴더), -가 있는 것은 파일이다.
- h 옵션을 붙이면 파일 크기를 해석하기 편하게 출력한다.
다음과 같이 명령하여 컴퓨터에 장착된 디스크와 파티션 목록을 출력할 수 있다.
# ls -l /dev/sd* brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 0 Oct 31 01:58 /dev/sda brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 1 Oct 31 01:58 /dev/sda1 brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 2 Oct 31 01:58 /dev/sda2 brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 16 Oct 31 01:58 /dev/sdb brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 17 Oct 31 02:34 /dev/sdb1
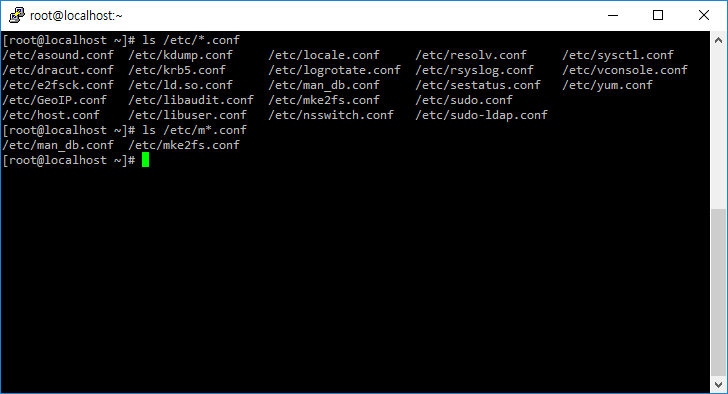
ls *
- *를 사용하여 특정 조건에 맞는 디렉토리와 파일만 출력할 수 있다.
- 다음과 같이 명령하면 /etc 디렉토리에서 확장자가 conf인 파일들을 출력한다.
# ls /etc/*.conf
- /etc 디렉토리에서 m으로 시작하고 확장자가 conf인 파일을 출력한다.
# ls /etc/m*.conf
ls --help
- ls 명령어의 옵션을 출력한다.
# ls --help
Usage: ls [OPTION]... [FILE]...
List information about the FILEs (the current directory by default).
Sort entries alphabetically if none of -cftuvSUX nor --sort is specified.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
-a, --all do not ignore entries starting with .
-A, --almost-all do not list implied . and ..
--author with -l, print the author of each file
-b, --escape print C-style escapes for nongraphic characters
--block-size=SIZE scale sizes by SIZE before printing them; e.g.,
'--block-size=M' prints sizes in units of
1,048,576 bytes; see SIZE format below
-B, --ignore-backups do not list implied entries ending with ~
-c with -lt: sort by, and show, ctime (time of last
modification of file status information);
with -l: show ctime and sort by name;
otherwise: sort by ctime, newest first
-C list entries by columns
--color[=WHEN] colorize the output; WHEN can be 'never', 'auto',
or 'always' (the default); more info below
-d, --directory list directories themselves, not their contents
-D, --dired generate output designed for Emacs' dired mode
-f do not sort, enable -aU, disable -ls --color
-F, --classify append indicator (one of */=>@|) to entries
--file-type likewise, except do not append '*'
--format=WORD across -x, commas -m, horizontal -x, long -l,
single-column -1, verbose -l, vertical -C
--full-time like -l --time-style=full-iso
-g like -l, but do not list owner
--group-directories-first
group directories before files;
can be augmented with a --sort option, but any
use of --sort=none (-U) disables grouping
-G, --no-group in a long listing, don't print group names
-h, --human-readable with -l, print sizes in human readable format
(e.g., 1K 234M 2G)
--si likewise, but use powers of 1000 not 1024
-H, --dereference-command-line
follow symbolic links listed on the command line
--dereference-command-line-symlink-to-dir
follow each command line symbolic link
that points to a directory
--hide=PATTERN do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN
(overridden by -a or -A)
--indicator-style=WORD append indicator with style WORD to entry names:
none (default), slash (-p),
file-type (--file-type), classify (-F)
-i, --inode print the index number of each file
-I, --ignore=PATTERN do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN
-k, --kibibytes default to 1024-byte blocks for disk usage
-l use a long listing format
-L, --dereference when showing file information for a symbolic
link, show information for the file the link
references rather than for the link itself
-m fill width with a comma separated list of entries
-n, --numeric-uid-gid like -l, but list numeric user and group IDs
-N, --literal print raw entry names (don't treat e.g. control
characters specially)
-o like -l, but do not list group information
-p, --indicator-style=slash
append / indicator to directories
-q, --hide-control-chars print ? instead of nongraphic characters
--show-control-chars show nongraphic characters as-is (the default,
unless program is 'ls' and output is a terminal)
-Q, --quote-name enclose entry names in double quotes
--quoting-style=WORD use quoting style WORD for entry names:
literal, locale, shell, shell-always, c, escape
-r, --reverse reverse order while sorting
-R, --recursive list subdirectories recursively
-s, --size print the allocated size of each file, in blocks
-S sort by file size
--sort=WORD sort by WORD instead of name: none (-U), size (-S),
time (-t), version (-v), extension (-X)
--time=WORD with -l, show time as WORD instead of default
modification time: atime or access or use (-u)
ctime or status (-c); also use specified time
as sort key if --sort=time
--time-style=STYLE with -l, show times using style STYLE:
full-iso, long-iso, iso, locale, or +FORMAT;
FORMAT is interpreted like in 'date'; if FORMAT
is FORMAT1FORMAT2, then FORMAT1 applies
to non-recent files and FORMAT2 to recent files;
if STYLE is prefixed with 'posix-', STYLE
takes effect only outside the POSIX locale
-t sort by modification time, newest first
-T, --tabsize=COLS assume tab stops at each COLS instead of 8
-u with -lt: sort by, and show, access time;
with -l: show access time and sort by name;
otherwise: sort by access time
-U do not sort; list entries in directory order
-v natural sort of (version) numbers within text
-w, --width=COLS assume screen width instead of current value
-x list entries by lines instead of by columns
-X sort alphabetically by entry extension
-1 list one file per line
SELinux options:
--lcontext Display security context. Enable -l. Lines
will probably be too wide for most displays.
-Z, --context Display security context so it fits on most
displays. Displays only mode, user, group,
security context and file name.
--scontext Display only security context and file name.
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
SIZE is an integer and optional unit (example: 10M is 10*1024*1024). Units
are K, M, G, T, P, E, Z, Y (powers of 1024) or KB, MB, ... (powers of 1000).
Using color to distinguish file types is disabled both by default and
with --color=never. With --color=auto, ls emits color codes only when
standard output is connected to a terminal. The LS_COLORS environment
variable can change the settings. Use the dircolors command to set it.
Exit status:
0 if OK,
1 if minor problems (e.g., cannot access subdirectory),
2 if serious trouble (e.g., cannot access command-line argument).
GNU coreutils online help: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>
For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'ls invocation'